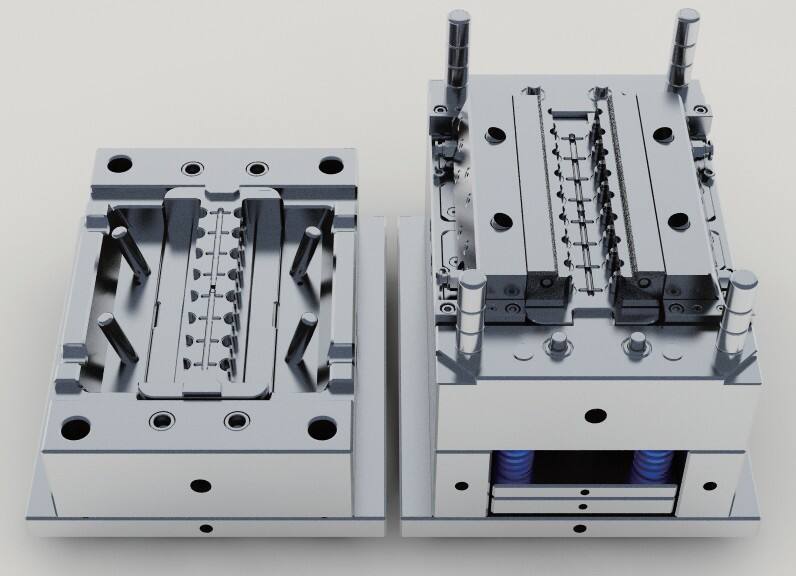
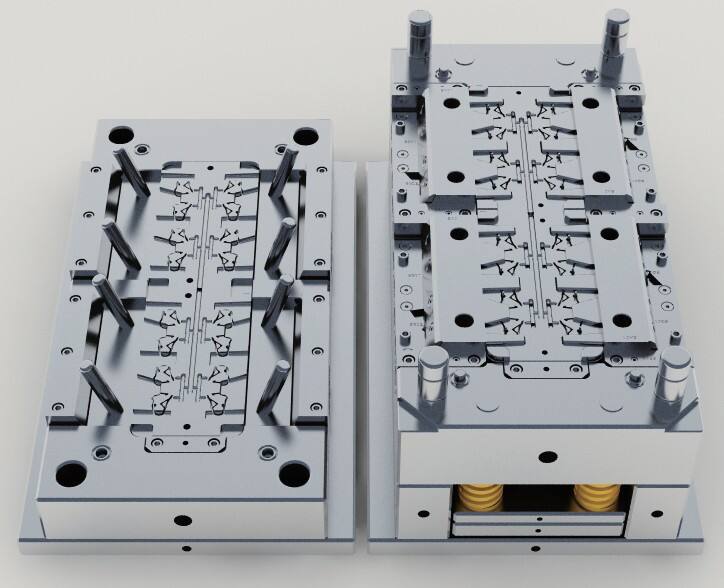
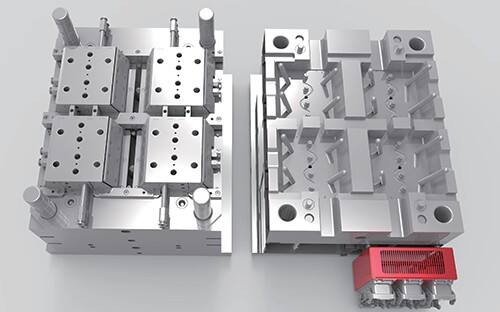
abs injection molding
ABS injection molding is a sophisticated manufacturing process that combines the versatility of ABS plastic with precision molding techniques. This process involves heating ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) pellets to their melting point and injecting the molten material into carefully designed molds under high pressure. The technology enables the production of complex geometric shapes with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. The process is particularly notable for its ability to maintain consistent quality across large production runs while offering excellent mechanical properties in the final products. ABS injection molding stands out for its capacity to produce parts with high impact resistance, good structural stability, and attractive surface aesthetics. The technology incorporates advanced temperature control systems and precise injection pressure management to ensure optimal material flow and cooling, resulting in products that exhibit minimal warping or shrinkage. This manufacturing method is widely employed in automotive components, consumer electronics housings, medical device casings, and various industrial applications where durability and aesthetic appeal are crucial requirements.