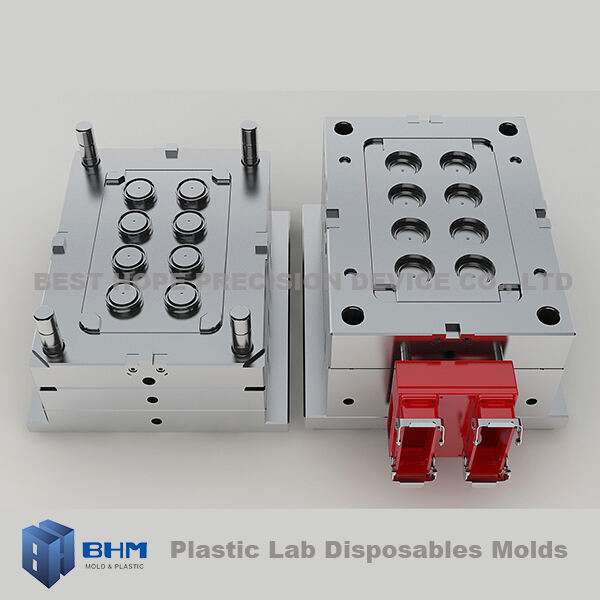
injection molding
Injection molding is a revolutionary manufacturing process that transforms plastic materials into precisely engineered products through a sophisticated system of heating, injecting, and cooling. This versatile technology operates by feeding plastic pellets into a heated barrel where they melt into a liquid state. The molten plastic is then forcefully injected into a custom-designed mold cavity under high pressure. Once inside the mold, the material cools and solidifies, taking on the exact shape of the cavity. This process can produce complex geometries with remarkable consistency and efficiency, making it ideal for both high-volume production runs and specialized manufacturing needs. The technology accommodates a wide range of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers, enabling the creation of products ranging from simple components to intricate medical devices. Modern injection molding machines incorporate advanced control systems that monitor and adjust crucial parameters such as temperature, pressure, and timing to ensure optimal product quality. The process has become indispensable in industries including automotive, consumer goods, electronics, and medical equipment manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision and repeatability in plastic part production.